
Sports Osteopathy
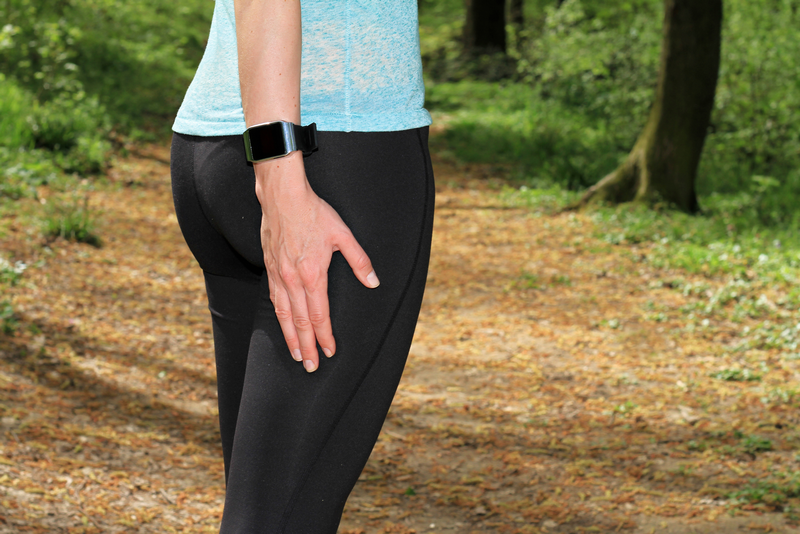

Sports injuries are common, particularly in contact sports where bruising and strains are part of the game. Osteopathy in the sporting field is rapidly being employed for elite athletes to casual participant and teams now using skills of osteopaths to help with their injured players; for example the number of sports clubs now employing osteopaths has increased significantly over the recent years. Sports players now depend on osteopathic medicine treatment as a way to heal and ease existing injuries and as a means of keeping their bodies in peak physical shape.
Common sports injuries include
- Muscle strains
- Joint sprains
- Groin injuries
- Shin splints
- Shoulder injuries
- Tennis and golfers elbow
- Achilles tendonopathy
- Knee problems (including cartilage and ligament injuries)
- Running injures
In sport, osteopathy identifies problems relating to the muscles, bones and tissues. This approach helps to identify wider issues that can contribute to localized pain or specific complaints.
Many of the injuries that occur when taking part in sports activities are the result of overuse i.e. playing too hard and too often e.g. tennis elbow, golfers elbow and bicep tendinitis or from not warming up properly beforehand or from not warming down after exercise. Injuries related to long distance running often include inflamed tendons, shin splints, aches and pains especially in hamstrings and the back. Osteopathy can resolve the injury and ease the pain, home exercises can also be recommended to speed of the healing process.
Repetitive strain injuries such as tennis elbow are caused by prolonged strain on a particular muscle or tendon. These injuries are not exclusive to tennis and also can be experienced in other sports or activities such as gardening, typing and playing an instrument. Treatment for repetitive strain injuries often involve specialized stretching and strengthening exercises.
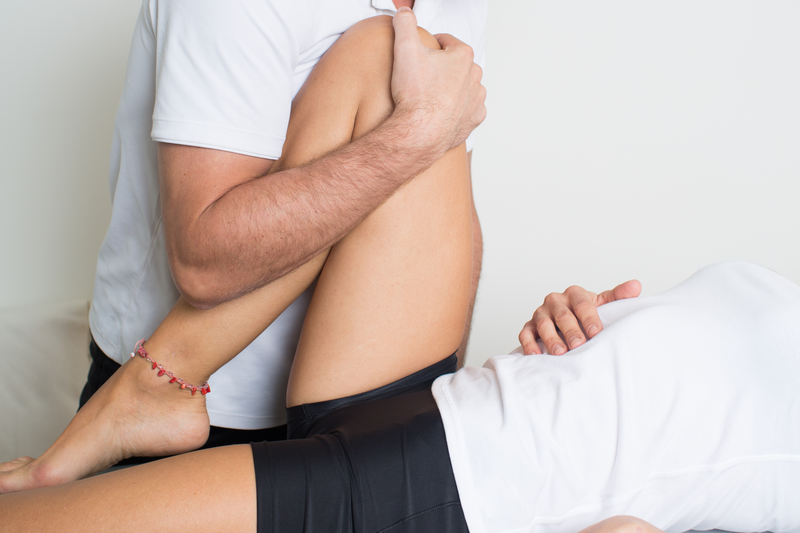

Young people especially are vulnerable in sport as their growing bodies are often expected to preform to high standards and they put exceptional physical demands on themselves. The good news is that although sports injuries are common, those who are fit tend to recover more quickly and easily from their injuries.
Sports specific assessment and techniques include
- Biomechanical assessment of movement
- Gait analysis
- Exercise prescription for rehabilitation and injury prevention
- Rehabilitation post-surgery
- Posture assessment
- Soft tissue techniques
- Joint mobilization and manipulation
- Taping to increase proprioception and facilitate recovery

